
“The power of our method is that it is extremely versatile and relatively non-disruptive,” says Xu.The use of osmotic blood brain barrier disruption is not reasonable and necessary when it is used as part of a treatment regimen for brain tumors. In addition to the substances tested for the study, Xu expects that scientists can use the LNPs to deliver a variety of therapeutic substances to the brain, including DNA and large-enzyme complexes. The GFP-Cre protein was the first-ever instance of genome editing of neuronal cells initiated intravenously. In the case of the tau antisense oligonucleotide, they observed a reduction in tau proteins. The team was able to confirm the successful targeting of these payloads to the mice’s brains. a tau antisense oligonucleotide that inhibits the production of the tau proteins associated with Alzheimer’s disease.amphotericin B, a small-molecule antifungal drug.Researchers from the Xu laboratory report the successful delivery of the following NT-lipidoid LNPs: When the LNPs arrive at the blood-brain barrier, their neurotransmitter provides entry, delivering the molecules they carry directly and safely to the brain’s neurons and other cells.Ĭo-author Feihe Ma notes that “It’s simple, effective, and potentially broadly applicable - we can modify the container for the drug, and by adding the NT-lipidoid, it’s like attaching an address label for delivery into the brain.” The scientists can inject the NT-lipidoid LNPs and the molecules they contain into the bloodstream intravenously. LNPs are small lipid bubbles into which the scientists inserted therapeutic molecules. Next, they doped these combined neurotransmitter-lipidoids, or NT-lipidoids, into lipid-nanoparticles (LNPs).

The authors of the study began by attaching one of these neurotransmitters to fat-, or lipid-like molecules. Xu and his colleagues have developed a system that uses a particular class of neurotransmitters as a means to traverse the barrier, carrying molecules into the brains of mice. However, the blood-brain barrier does allow certain neurotransmitters into the brain. However, adapting these materials for such use is often complicated. Scientists have also investigated a similar use of polymers, nanocapsules, and nanoparticles with some success. However, cost and safety concerns accompany this approach. Researchers have looked into the use of “carriers,” such as monoclonal antibodies and modified viruses, that travel into the brain, taking therapeutic molecules with them. Direct injection of compounds into the brain, as well as efforts to force ‘leaks’ through the barrier, carry risks, such as neurotoxicity, infection, and tissue damage. Scientists have attempted various workarounds, and none have proven sufficiently safe or effective. While s mall molecule or macromolecule drugs have the potential to treat brain tumors, infections, neurogenerative disorders, and stroke, the presence of the blood-brain barrier makes it difficult for doctors to administer such therapies. The barrier is highly selective about the non-native molecules it allows into the brain, and that includes therapeutic substances.
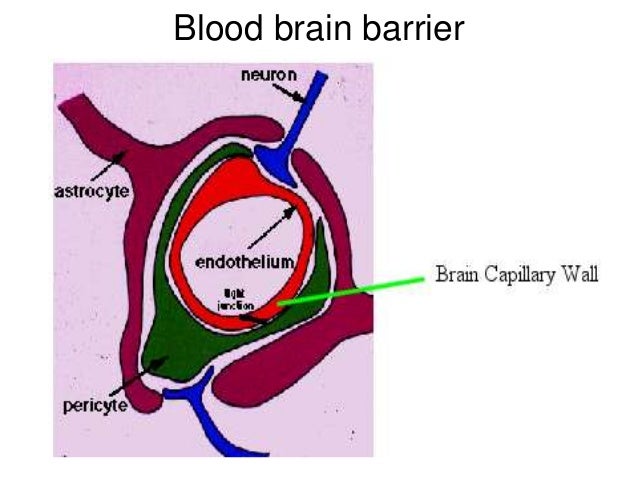
The blood-brain barrier consists of a blood vessel lining of endothelial cells that keeps foreign molecules from escaping from the blood vessels and entering the brain fluid where they could affect neurons and other brain cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
